Building a SatNOGs Ground Station in Egypt
Project Overview
Project: Development of a SatNOGs fixed ground station with two Power Distribution Units (PDUs) to support a future rotator system.
Organization: Outlyer.space
Timeline: February – September 2025 (~30 weeks)

Introduction
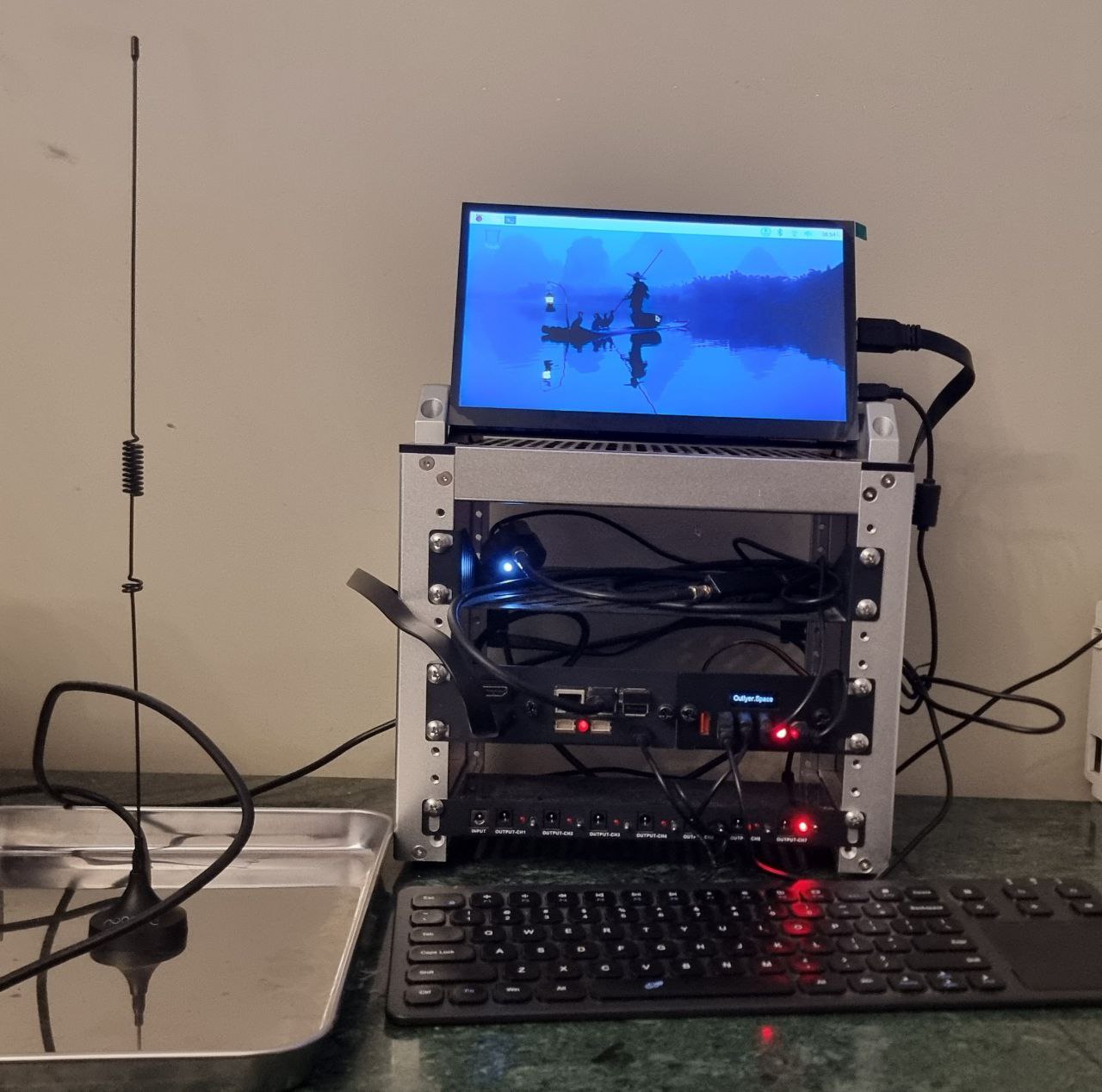
This post documents the final build of a SatNOGs omnidirectional ground station in Egypt, created during my internship with Outlyer.space.
Originally planned as a 5–6 week project, it evolved into a 30-week effort due to hardware challenges, shipping delays, and power distribution issues.
If you’re new to SatNOGs, it’s an open-source, global network of satellite ground stations. This project gave me hands-on experience with antennas, SDRs, and ground station operation — as well as navigating Egyptian customs for importing electronics.
Software Setup
The software stack follows the SatNOGs deployment model:
- Prepare the Raspberry Pi
- Download the SatNOGs 64-bit stable image from the SatNOGs Raspberry Pi Image Repository.
- Verify the image integrity using SHA256.
- Flash the image to the SD card using Raspberry Pi Imager:
- Select your Raspberry Pi model.
- Provide the image path.
- Configure Wi-Fi, locale, SSH, and create a user account.
- Initial Boot
- Insert the SD card into the Raspberry Pi and power it on.
- Login with the credentials set earlier.
- Update the system:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
- Install & Configure SatNOGs Client
- Run
sudo satnogs-setupto start the configuration menu. - Register on SatNOGs Network and obtain your API token.
- In
satnogs-setup, enter:- SATNOGS_API_TOKEN
- SATNOGS_STATION_ID, LAT, LON, ELEV
- SATNOGS_SOAPY_RX_DEVICE =
driver=rtlsdr - SATNOGS_RX_SAMP_RATE =
2.048e6 - SATNOGS_RX_GAIN (adjust per satellite)
- Run
- Gain Calibration
- Connect the SDR and use a tool like CubicSDR to experiment with gain and noise levels:
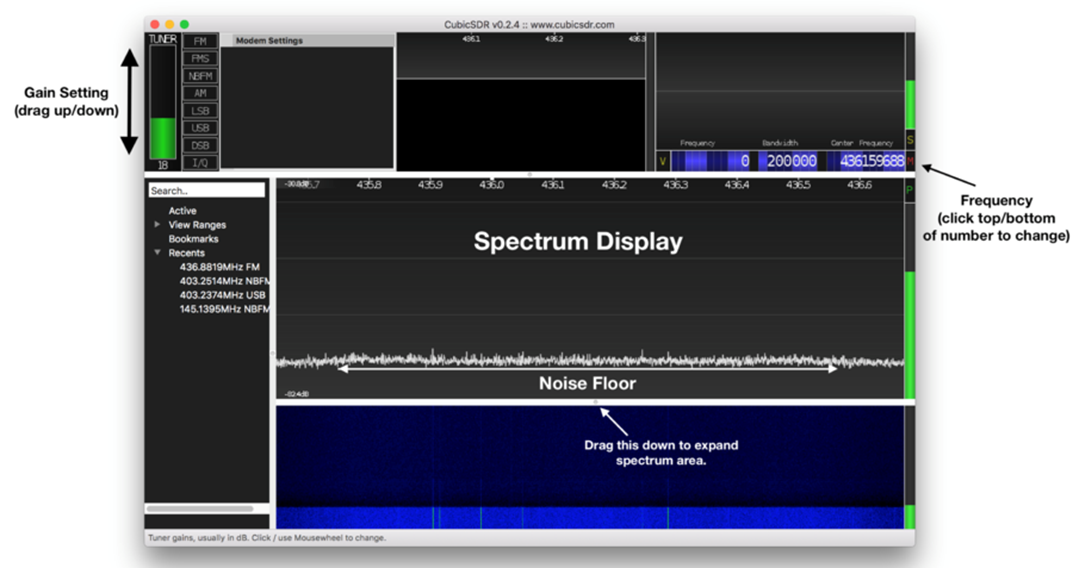
(Extra) Desktop Enivroment - The SatNOGs images are server optimized with no GUI enviroment. To install a desktop enviroment run: - sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade –y to update the system - sudo apt install raspberrypi-ui-mods –y install Raspberry Pi PIXEL Desktop - Enable GUI on boot: - sudo raspi-config - Go to System Options > Boot / Auto Login - Choose Desktop Autologin or just Desktop
Hardware
Bill of Materials
| Component | Model / Link | Purpose | Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antenna | Bingfu Omni, VHF (136-174 MHz) & UHF (400-470 MHz) | Receiving satellite signals; suitable for non-rotary builds | 10.00 |
| Low Noise Amplifier (LNA) | NooElec Inline LNA v2 | Signal amplification | 35.00 |
| SDR Receiver | NooElec NESDR SMArt v5 | RF signal reception | 37.95 |
| Controller | Raspberry Pi 5 (8 GB) | Running SatNOGs client software | 93.80 |
| Power Distribution Unit (PDU) 1 | DeskPi DC PDU Lite | Original PDU for 12 V / mixed loads | 50.00 |
| Power Distribution Unit (PDU) 2 | 52Pi 4-Channel 5 V PDU | Stable 5 V power for Raspberry Pi and peripherals | 17.50 |
| Rack Mount | DeskPi RackMate | Enclosure for station hardware | 80.00 |
| Bracket | DeskPi DP-0039 Bracket | Mounts Raspberry Pi + new PDU | 40.00 |
| Display | GeeekPi 10.1-inch LCD Screen | Display screen for desktop environment | 69.99 |
The final hardware build integrates dual PDUs to solve earlier power issues:
- Antenna: Omnidirectional, mounted on the building roof.
- Signal Chain: Antenna → LNA → NooElec SDR → Raspberry Pi 5.
- Power:
- The original DeskPi PDU remains for 12 V and mixed loads.
- The new 52Pi 5 V PDU exclusively powers the Raspberry Pi, LNA, and LCD screen.
- Both the Pi and PDU are mounted using the DeskPi DP-0039 bracket for stability and modularity.
Assembly
First, assemble the DeskPi Rackmount following the included 14-page manual (6 steps). A YouTube guide is also available, though not necessary due to the straightforward assembly.
Next, install the DeskPi Rackmate 10-inch 1U Rack, designed for the Raspberry Pi 5. It provides a robust and efficient housing solution for both the EP-0249 PDU(52Pi 4-USB Channel PDU) and Raspberry Pi. Connect the 52Pi 4-USB Channel PDU to power the 5 V components, LCD screen, LNA and Pi.
For more information about the EP-0249 PDU, consult the wiki — it includes detailed information on the built-in Raspberry Pi Pico I²C LCD display of the PDU.
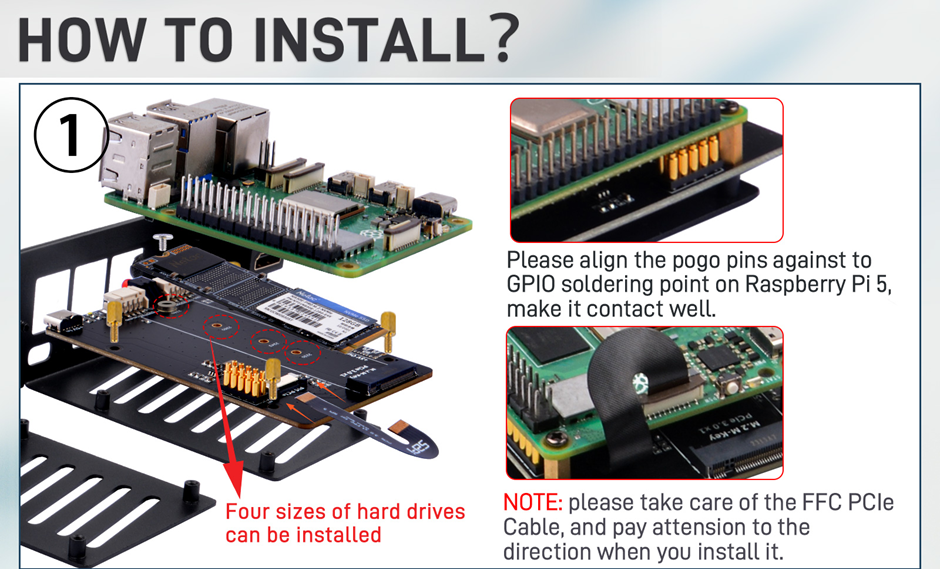
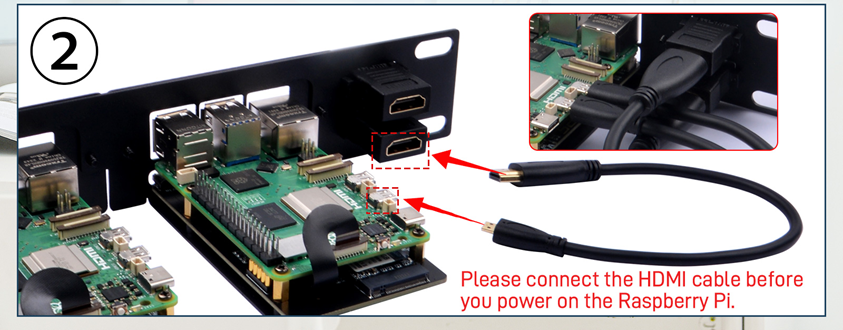

Finally assemble the LCD Display and place it on top of the mount, wire everything together and your station should be up and running. If not checkout the trouble shooting page of the SatNOGS Wiki, https://wiki.satnogs.org/Troubleshooting.

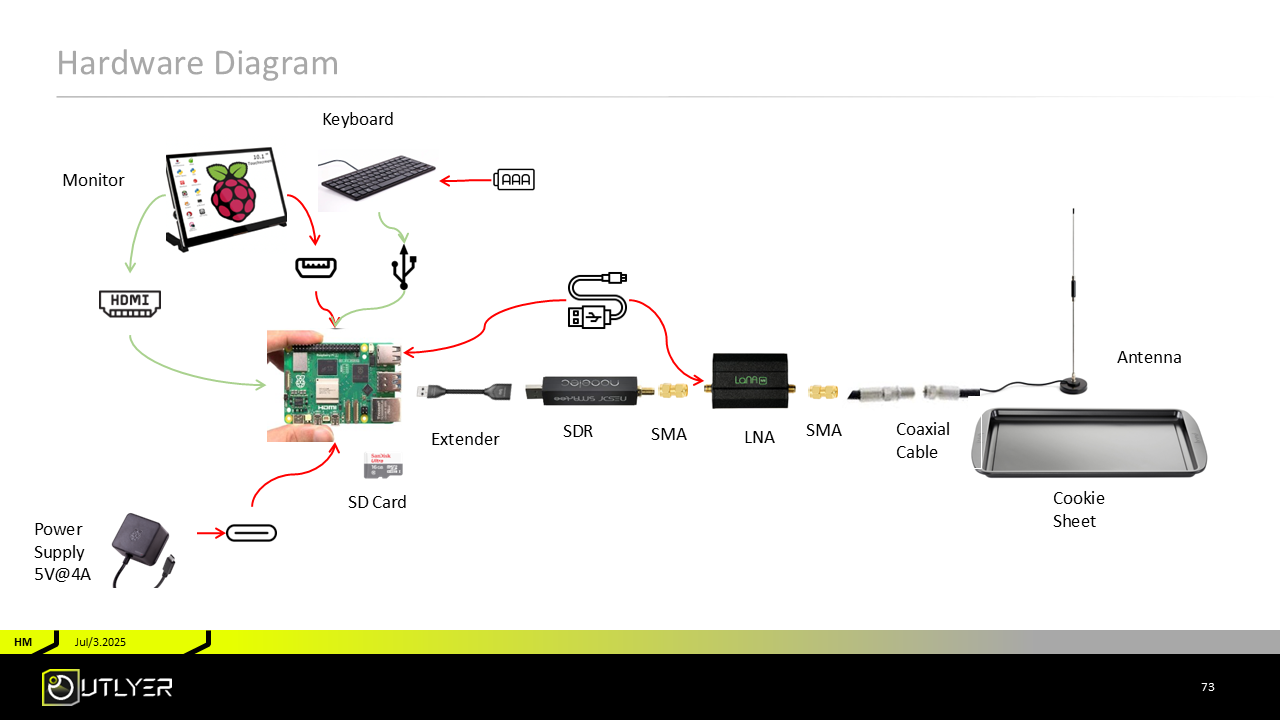
This configuration isolates sensitive 5 V components, ensures stable operation, and leaves room for a future rotator upgrade without redesigning the power system.
Challenges & Lessons Learned
While the final build works reliably, the path to get here involved several challenges:
- Shipping Delays
- Importing electronics to Egypt often took weeks per component. This extended the timeline far beyond the initial 6-week plan.
- Power Delivery Issues in the First Build
- The initial setup used only the DeskPi PDU Lite.
- Its ~0.4 V drop per channel prevented the Raspberry Pi from booting even with a 10 A adapter.
- DeskPi support confirmed it was not intended for 5 V loads, prompting the switch to the 52Pi PDU.
These lessons underscore the importance of local sourcing and voltage verification when designing ground stations.
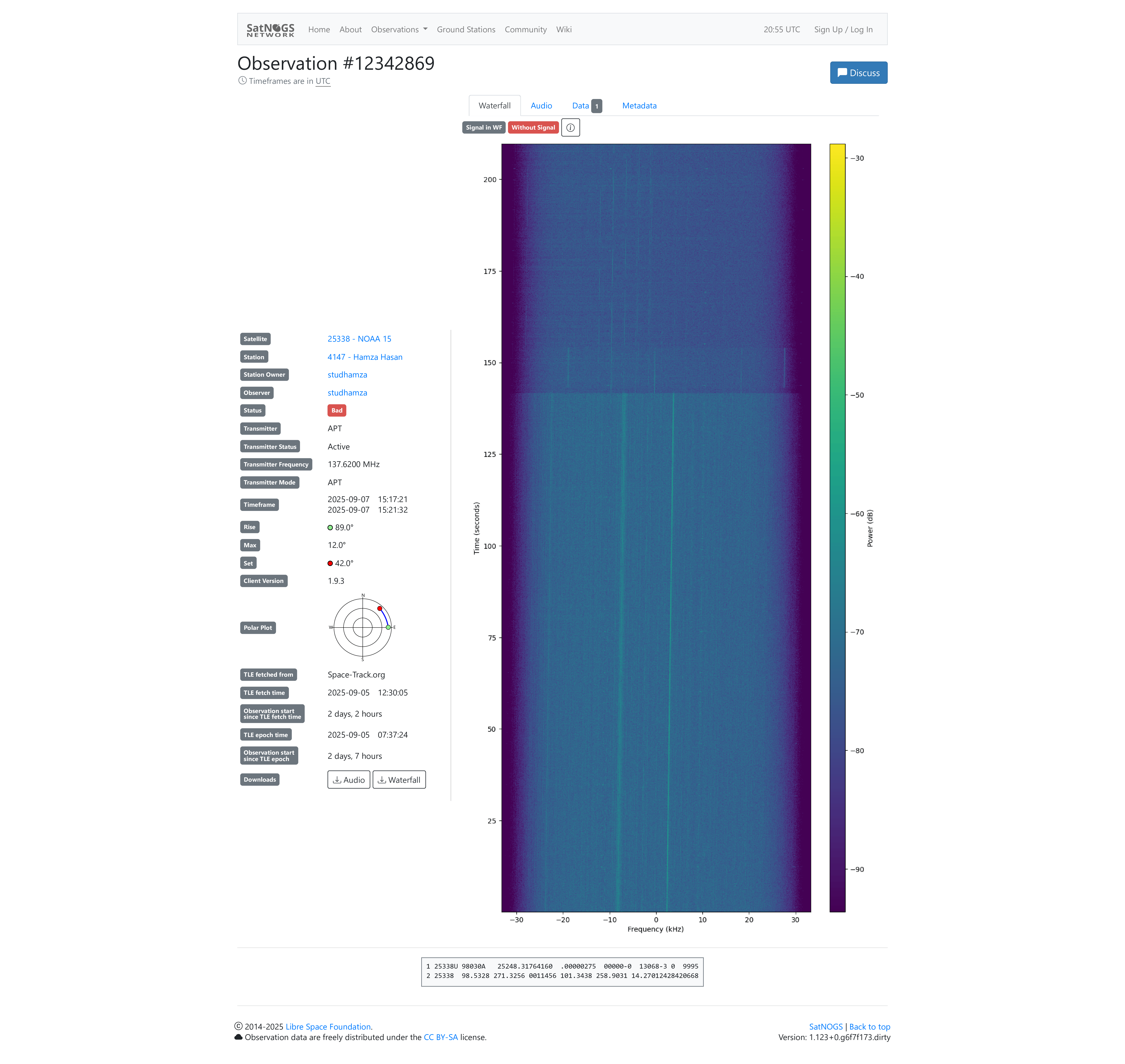
Performance: NOAA Satellite Reception
From a 5th-floor urban location, an omnidirectional antenna has limited reception compared to directional or rotator-based systems. However, the station successfully captured faint NOAA signals visible in the waterfall plot below:
Useful Links
Thanks for reading! Feedback and suggestions from the SatNOGs community are very welcome — especially regarding improving reception from an omnidirectional setup in an urban environment.
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: