FM Receiver with GNU Radio- Week 3
FM Receiver App – Week 3 Update
This week, I made progress in the following features:
- Integrating GNU Radio flowgraphs to python application
- Changing the UI according to community suggestions
- Rearrange Directory Structure
Creating Simple FM Receiver
First, lets start with a simple FM Receiver; following the tutorial.
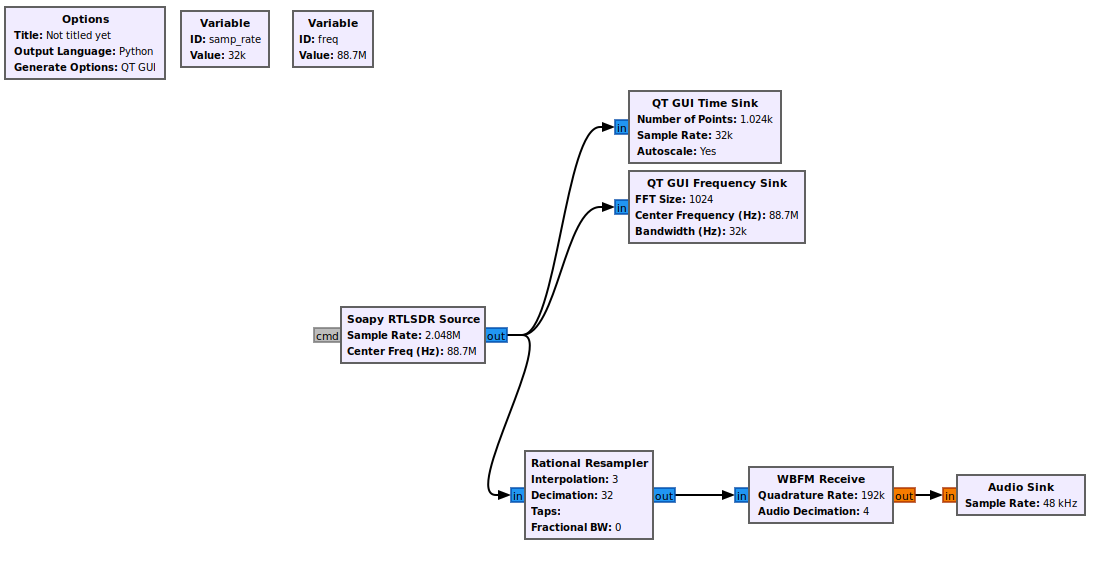
Looking into the code
Every flowgraph (GRC) file generates a python file, inorder to integrate the flowgraph into the application we first need to take a look at the generated code.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
#
# SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-3.0
#
# GNU Radio Python Flow Graph
# Title: Not titled yet
# GNU Radio version: 3.10.1.1
from gnuradio import analog
from gnuradio import audio
from gnuradio import filter
from gnuradio.filter import firdes
from gnuradio import gr
from gnuradio.fft import window
import sys
import signal
from argparse import ArgumentParser
from gnuradio.eng_arg import eng_float, intx
from gnuradio import eng_notation
from gnuradio import soapy
class simple_fm_receiver(gr.top_block):
def __init__(self):
gr.top_block.__init__(self, "Not titled yet", catch_exceptions=True)
##################################################
# Variables
##################################################
self.freq = freq = 88700000
##################################################
# Blocks
##################################################
self.soapy_rtlsdr_source_0 = None
dev = 'driver=rtlsdr'
stream_args = ''
tune_args = ['']
settings = ['']
self.soapy_rtlsdr_source_0 = soapy.source(dev, "fc32", 1, '',
stream_args, tune_args, settings)
self.soapy_rtlsdr_source_0.set_sample_rate(0, 2.048*10**6)
self.soapy_rtlsdr_source_0.set_gain_mode(0, True)
self.soapy_rtlsdr_source_0.set_frequency(0, freq)
self.soapy_rtlsdr_source_0.set_frequency_correction(0, 0)
self.soapy_rtlsdr_source_0.set_gain(0, 'TUNER', 20)
self.rational_resampler_xxx_0 = filter.rational_resampler_ccc(
interpolation=3,
decimation=32,
taps=[],
fractional_bw=0)
self.audio_sink_0 = audio.sink(48000, '', True)
self.analog_wfm_rcv_0 = analog.wfm_rcv(
quad_rate=4*48*10**3,
audio_decimation=4,
)
##################################################
# Connections
##################################################
self.connect((self.analog_wfm_rcv_0, 0), (self.audio_sink_0, 0))
self.connect((self.rational_resampler_xxx_0, 0), (self.analog_wfm_rcv_0, 0))
self.connect((self.soapy_rtlsdr_source_0, 0), (self.rational_resampler_xxx_0, 0))
def get_freq(self):
return self.freq
def set_freq(self, freq):
self.freq = freq
self.soapy_rtlsdr_source_0.set_frequency(0, self.freq)
def main(top_block_cls=simple_fm_receiver, options=None):
tb = top_block_cls()
def sig_handler(sig=None, frame=None):
tb.stop()
tb.wait()
sys.exit(0)
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, sig_handler)
signal.signal(signal.SIGTERM, sig_handler)
tb.start()
try:
input('Press Enter to quit: ')
except EOFError:
pass
tb.stop()
tb.wait()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Our main focus here is on the object created in the main function top_block_cls=simple_fm_receiver and it’s functions, more specifically the set_freq function. We will be using this to instaniate the object and control the frequency.
Integration with python
Before moving on onto the next part, assuming youre using a python virtual enviroment like mine I am you first need to tell it where to look for the GNU Radio python libraries and file. To do so you need to have GNU Radio installed on your system and run this command:
python3 -m venv --system-site-packages
For further information, refer to this email: Re: Integrating GRC-Generated Python Code into Python Virtual Environmen
Now time to work, simply put I followed and will always follow these 3 steps:
- Import object (simple_fm_receiver) from flowgraph.py file
- Instantiate object in main window class,
self.simple_fm_receiver = simple_fm_receiver() - Use simple_fm_receiver methodes, like start/stop/set_freq to control the flograph and its elements/variables.
GUI Change
Its easier to show the new UI than to describe the changes:
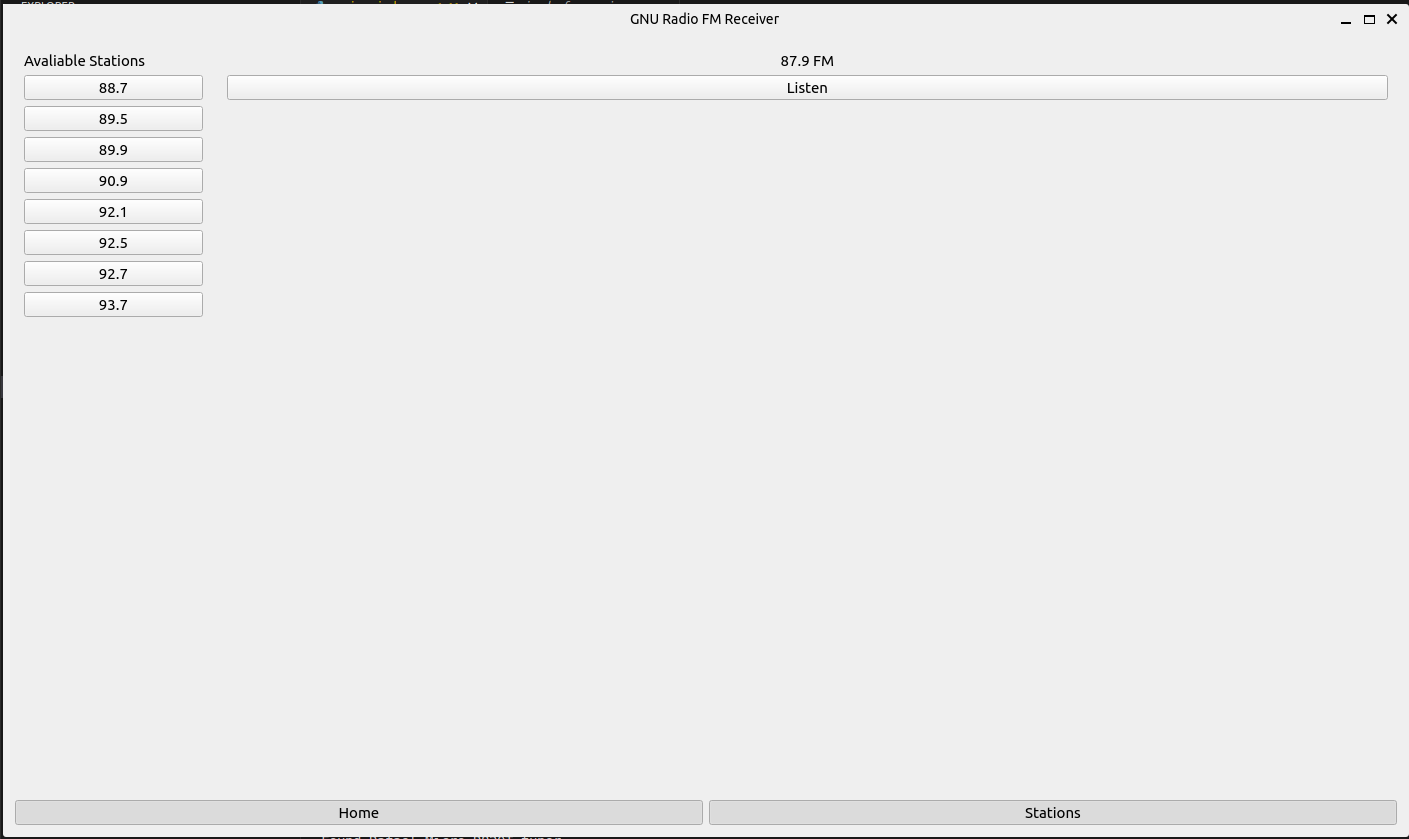
It was inspired by simplistic design recommended from this series of email from the mailing list: Re: Feedback Wanted: UI of FM receiver GsoC project
What’s Next?
For next week, I’m planning to:
- RDS integration
- Frequency scanning & Channel Listing
- Advanced/Debug view
Links
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: